- 2023-01-27 21:01:26
- 7353 热度
- 0 评论
本示例使用SpringBoot进行配置和编码。

引入依赖:
<dependencies> <!-- 核心模块,包括自动配置支持、日志和YAML --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 测试模块,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- 日志依赖(TRANCE < DRBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR <FATAL < OFF) --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 支持web --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.auth0</groupId> <artifactId>java-jwt</artifactId> <version>3.4.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
因为示例仅使用JWT,所以这里定义两个注解类用来标记那个方法是需要验证那个不需要:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 用来跳过验证的PassToken
*/
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PassToken {
boolean required() default true;
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 需要登录才能进行操作的注解UserLoginToken
*
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface UserLoginToken {
boolean required() default true;
}
@Target:注解的作用目标
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)——接口、类、枚举、注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)——字段、枚举的常量
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)——方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)——方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) ——构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)——局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)——注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE)——包
@Retention:注解的保留位置
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:这种类型的Annotations只在源代码级别保留,编译时就会被忽略,在class字节码文件中不包含。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS:这种类型的Annotations编译时被保留,默认的保留策略,在class文件中存在,但JVM将会忽略,运行时无法获得。
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:这种类型的Annotations将被JVM保留,所以他们能在运行时被JVM或其他使用反射机制的代码所读取和使用。
@Document:说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中
@Inherited:说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解
实体对象,为了示例简单,这个对象就当作自己的service了:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWT;
import com.auth0.jwt.algorithms.Algorithm;
@Service
public class User {
String Id = "0";
String username = "admin";
String password = "1";
public User getUserById(String id) {
return new User();
}
public String getToken(User user) {
String token="";
token= JWT.create().withAudience(user.getId()).sign(Algorithm.HMAC256(user.getPassword()));
return token;
}
public String getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
Algorithm.HMAC256():使用HS256生成token,密钥则是用户的密码,唯一密钥的话可以保存在服务端。
withAudience()存入需要保存在token的信息,这里把用户ID存入token中。
写一个拦截器去获取token并验证token
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWT;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWTVerifier;
import com.auth0.jwt.algorithms.Algorithm;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTDecodeException;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTVerificationException;
public class AuthenticationInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private User userSer;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse,
Object object) throws Exception {
String token = httpServletRequest.getHeader("token");// 从 http 请求头中取出 token
// 如果不是映射到方法直接通过
if (!(object instanceof HandlerMethod)) {
return true;
}
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) object;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
// 检查是否有passtoken注释,有则跳过认证
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(PassToken.class)) {
PassToken passToken = method.getAnnotation(PassToken.class);
if (passToken.required()) {
return true;
}
}
// 检查有没有需要用户权限的注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(UserLoginToken.class)) {
UserLoginToken userLoginToken = method.getAnnotation(UserLoginToken.class);
if (userLoginToken.required()) {
// 执行认证
if (token == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("无token,请重新登录");
}
// 获取 token 中的 user id
String userId;
try {
userId = JWT.decode(token).getAudience().get(0);
} catch (JWTDecodeException j) {
throw new RuntimeException("401");
}
User user = userSer.getUserById(userId);
if (user == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("用户不存在,请重新登录");
}
// 验证 token
JWTVerifier jwtVerifier = JWT.require(Algorithm.HMAC256(user.getPassword())).build();
try {
jwtVerifier.verify(token);
} catch (JWTVerificationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("401");
}
return true;
}
}
return true;
}
}
实现一个拦截器就需要实现HandlerInterceptor接口
HandlerInterceptor接口主要定义了三个方法
1.boolean preHandle ():
预处理回调方法,实现处理器的预处理,第三个参数为响应的处理器,自定义Controller,返回值为true表示继续流程(如调用下一个拦截器或处理器)或者接着执行
postHandle()和afterCompletion();false表示流程中断,不会继续调用其他的拦截器或处理器,中断执行。
2.void postHandle():
后处理回调方法,实现处理器的后处理(DispatcherServlet进行视图返回渲染之前进行调用),此时我们可以通过modelAndView(模型和视图对象)对模型数据进行处理或对视图进行处理,modelAndView也可能为null。
3.void afterCompletion():
整个请求处理完毕回调方法,该方法也是需要当前对应的Interceptor的preHandle()的返回值为true时才会执行,也就是在DispatcherServlet渲染了对应的视图之后执行。用于进行资源清理。整个请求处理完毕回调方法。如性能监控中我们可以在此记录结束时间并输出消耗时间,还可以进行一些资源清理,类似于try-catch-finally中的finally,但仅调用处理器执行链中
主要流程:
1.从 http 请求头中取出 token,
2.判断是否映射到方法
3.检查是否有passtoken注释,有则跳过认证
4.检查有没有需要用户登录的注解,有则需要取出并验证
5.认证通过则可以访问,不通过会报相关错误信息
配置拦截器
在配置类上添加了注解@Configuration,标明了该类是一个配置类并且会将该类作为一个SpringBean添加到IOC容器内。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* 配置那些资源需要验证
*/
@Configuration
public class InterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(authenticationInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**");
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationInterceptor authenticationInterceptor() {
return new AuthenticationInterceptor();
}
}
这里拦截所有请求。
编写接口代码,登录接口一般是不验证的。在getMessage()中加上了登录注解,说明该接口必须登录获取token后,在请求头中加上token并通过验证才可以访问。
示例先通过/login获取token,注意这个接口不做任何处理,仅为示例,然后请求头中增加token字段为请求到的值。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class UserApi {
@Autowired
private User userSer;
/**
* 不需要验证,获取token,正常的话这是登录接口,需要验证用户名密码,验证成功后才会生成token,示例写死
*/
@GetMapping("/login")
@ResponseBody
public String login() {
User user = userSer.getUserById("0");
String token = user.getToken(user);
return token;
}
/**
* 需要验证,有token才能请求到这个接口
*/
@UserLoginToken
@GetMapping("/getMessage")
@ResponseBody
public String getMessage() {
return "恭喜您,访问成功";
}
}
启动后访问接口http://localhost:8080/login 获取到token
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJhdWQiOiIwIn0.5dWGdyLwQ2-ji7Ri-rJ7OjPC0Q4FsP-74MRYwM005lc。
然后使用restclient增加一个请求头
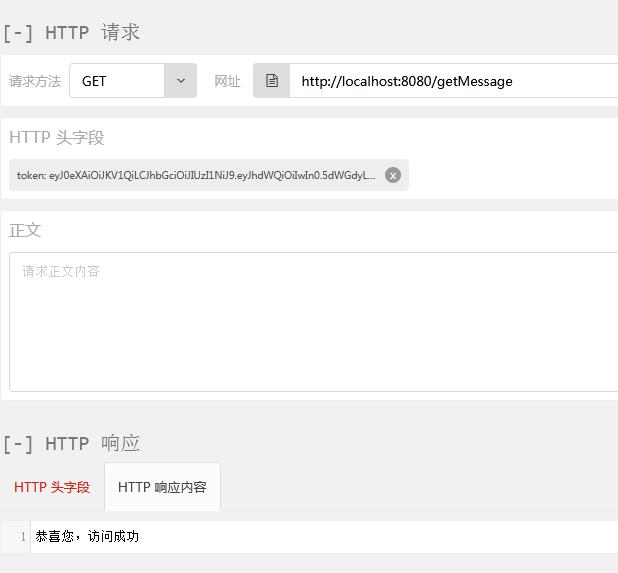
如果直接访问这个接口的话,工程报错,不能访问。
- Spring(403)
- Boot(208)
- Spring Boot(187)
- Spring Cloud(82)
- Java(82)
- Cloud(82)
- Security(60)
- Spring Security(54)
- Boot2(51)
- Spring Boot2(51)
- Redis(31)
- SQL(29)
- Mysql(25)
- IDE(24)
- Dalston(24)
- MVC(22)
- JDBC(22)
- IDEA(22)
- mongoDB(22)
- Web(21)
- CLI(20)
- SpringMVC(19)
- Alibaba(19)
- Docker(17)
- SpringBoot(17)
- Git(16)
- Eclipse(16)
- Vue(16)
- Apache(15)
- ORA(15)
- JPA(15)
- Tomcat(14)
- Linux(14)
- HTTP(14)
- Mybatis(14)
- Oracle(14)
- jdk(14)
- Nacos(13)
- Pro(13)
- XML(13)
- JdbcTemplate(13)
- OAuth(13)
- OAuth2(12)
- Data(12)
- JSON(12)
- Myeclipse(11)
- stream(11)
- int(11)
- not(10)
- Bug(10)
- Hystrix(9)
- ast(9)
- maven(9)
- Map(9)
- Swagger(8)
- APP(8)
- API(8)
- Bit(8)
- session(8)
- Window(8)
- too(7)
- HTML(7)
- Github(7)
- JavaMail(7)
- Cache(7)
- File(7)
- IntelliJ(7)
- mail(7)
- windows(7)
- ehcache(6)
- UDP(6)
- RabbitMQ(6)
- star(6)
- and(6)
- Excel(6)
- pushlet(6)
- Log4J(6)
- apt(6)
- Freemarker(6)
- read(6)
- WebFlux(6)
- JSP(6)
- Bean(6)
- error(6)
- Server(6)
- nginx(6)
- jar(6)
- ueditor(6)
- for(5)
- DOM(5)
- Sentinel(5)
- the(5)
- JWT(5)
- rdquo(5)
- PHP(5)
- Struts(5)
- string(5)
- script(5)
- Syntaxhighlighter(5)
- Tool(5)

